SAP SD migration from ECC to S/4HANA requires more than a technical system upgrade. It involves redesigning core Sales and Distribution processes, aligning master data with the Business Partner model, and validating pricing, credit, and order-to-cash flows. This guide provides a structured, phase-by-phase approach to planning and executing an SAP S/4HANA SD migration with reduced risk and predictable outcomes.
From Transaction to Insight: The SAP S/4HANA SD Evolution
Upgrading SAP Sales and Distribution from ECC to S/4HANA transforms it from a complex, transaction-based system into a streamlined and intelligent platform. Core processes remain familiar, but key innovations redefine its capabilities.
S/4HANA empowers businesses with AI-driven automation, real-time analytics, and cloud agility, building a compliant, competitive foundation for the future.
The shift centers on simplification and speed. A unified Business Partner model replaces separate customer and vendor records. Most importantly, the move to an in-memory database enables real-time analytics, providing instant business insights. For users, the modern SAP Fiori interface replaces the classic GUI, offering a simpler, more intuitive experience.
Ultimately, this is an evolution from managing transactions to driving strategic insight with greater agility and clarity.
ECC to S4 HANA migration
Transitioning your SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) operations from ECC to S/4HANA is more than a technical upgrade – it’s a strategic transformation. While the path offers flexibility through brownfield (system conversion) or greenfield (new implementation) approaches, the core of the journey lies in mastering S/4HANA’s simplified data architecture and real-time capabilities.
This evolution requires moving beyond familiar ECC constructs. You will replace the legacy customer master with the unified Business Partner (BP) model, consolidate transactional tables like VBUK and VBUP, and migrate to the modern pricing foundation (PRCD_ELEMENTS). Successfully navigating these changes is critical to unlocking streamlined processes and deeper business insights.
This guide provides a complete, professional roadmap for migrating SAP Sales & Distribution (SD) processes from ECC to S/4HANA. It highlights key changes in:
- Pricing & Condition Techniques
- Billing & Output Management
- Business Partner Conversion
- ATP & Order Management Enhancements
- Logistics Execution Improvements
- FSCM Credit Management
- EDI & Integration Refinements
- Condition Contract Management (CCM) replacing legacy rebates
It is tailored for SD Solution Architects, Project Managers, Functional Consultants, and Enterprise Leaders overseeing an S/4HANA transformation.
Step-by-Step Guide: Migrating from SAP ECC to SAP S/4HANA SD
This guide provides a complete and practical roadmap for migrating SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) processes from ECC to S/4HANA. It explains functional, technical, and data-related changes introduced with S/4HANA SD and outlines how organizations can plan, design, build, test, and stabilize their SD landscape during transformation.
This guide is intended for SD Solution Architects, Project Managers, Functional Consultants, and enterprise leaders who are actively planning or executing an SAP S/4HANA migration. It is best used during project preparation, blueprinting, and delivery phases to validate scope, identify risks, and align teams on expected changes.
1. Migration Approaches – Choosing the Right Path for SD
SAP SD migration from ECC to S/4HANA can follow different approaches depending on system complexity and business goals.
1.1 System Conversion (Brownfield)
System conversion is the most commonly used approach for SD migration. It allows organizations to move their existing ECC system to S/4HANA while preserving current business processes and historical data.
This approach is suitable when organizations want to retain:
- Existing pricing procedures
- Sales orders, deliveries, and billing flows
- Smart Forms and SAPscript outputs
- EDI and IDoc integrations
- Legacy partner functions and sales structures
- Credit management processes (migrated to FSCM)
Brownfield conversion minimizes disruption and reduces implementation timelines.
1.2 New Implementation (Greenfield)
A greenfield implementation is ideal for organizations that want to redesign and standardize their SD processes.
This approach is recommended when the objective is to:
- Redesign global pricing structures
- Implement advanced ATP and backorder processing
- Introduce new billing models such as subscription or usage-based billing
- Harmonize customer master data using the Business Partner model
- Replace legacy rebates with Condition Contract Management
1.3 Selective Data Transition (Hybrid)
Selective data transition is well suited for multi-entity organizations that require partial migration.
This approach works best when:
- Only selected sales organizations or channels are migrated
- Historical SD data must be selectively retained
- Phased or regional rollouts are required
- Multiple ECC systems are being consolidated
2. High-Level Phases of SD Migration
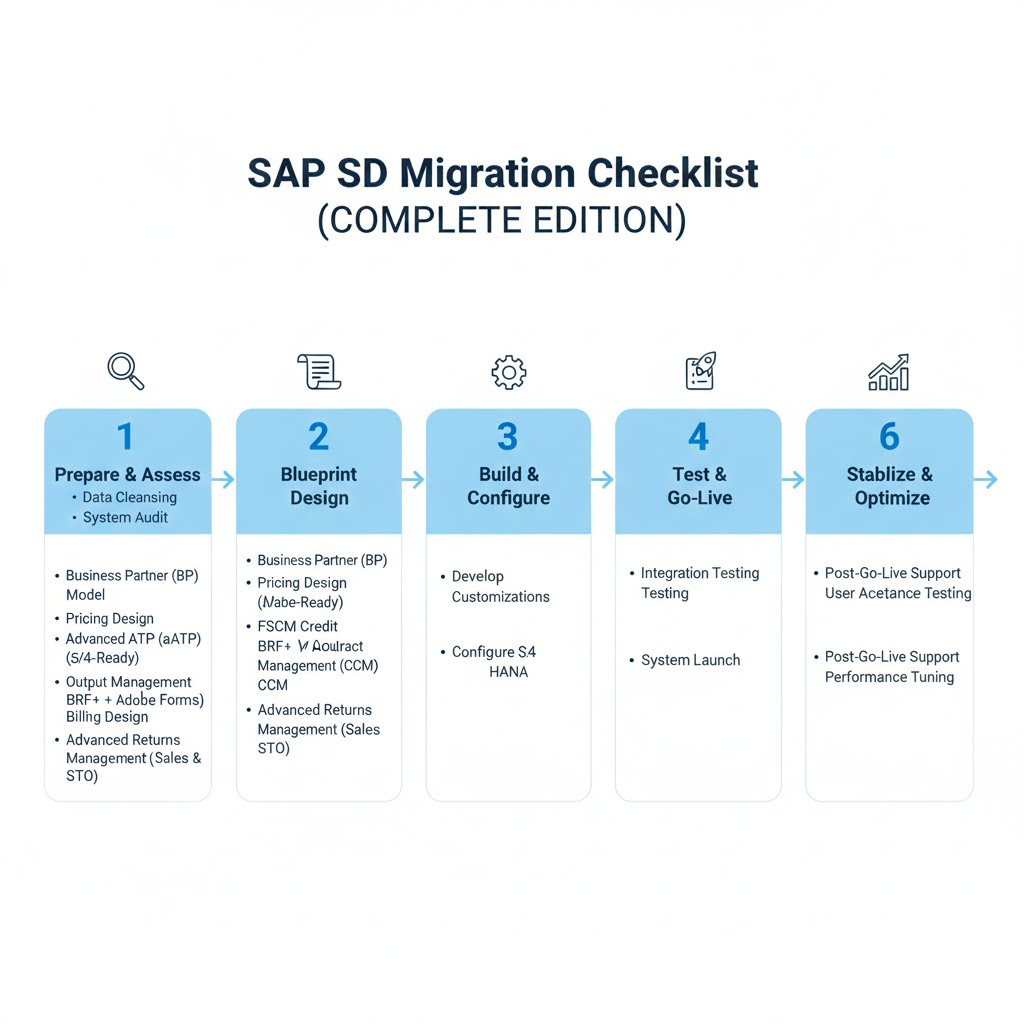
An SAP S/4HANA SD migration typically follows six structured phases:
- Prepare and Assess
- Blueprint and Design
- Build and Configure
- Test and Validate
- Cutover and Go-Live
- Stabilize and Optimize
Each phase includes SD-specific functional, technical, and data-related activities.
3. Phase-by-Phase SD Migration Checklist
This best-practice checklist provides a reliable framework for your SD migration, guiding you through each critical phase: planning, execution, validation, and post-migration optimization.
3.1 Phase 1 – Prepare and Assess
Early assessment is critical in SAP SD migration from ECC to S/4HANA to avoid downstream rework.The objective of this phase is to understand the impact of S/4HANA on existing SD processes and prepare the system for migration.
Key assessment areas include:
- Pricing conditions, discounts, and tax determination
- Rebate agreements and migration to Condition Contract Management
- ATP logic and availability checks
- Delivery, shipment, and billing processes
- Output management and form technologies
- EDI and IDoc interfaces
- Credit management migration from FI-AR to FSCM
Simplification items to consider:
- Customer master replaced by Business Partner model
- ECC rebates replaced by Condition Contract Management
- FI-based credit management replaced by FSCM
- Smart Forms replaced by Adobe Forms
- ATP redesigned using aATP
- Pricing data model changes
Custom code review should focus on:
- User exits and enhancements
- Custom pricing routines
- Custom IDocs and interfaces
Deliverables of this phase include an SD readiness report, simplification item register, and SD impact analysis.
Common pitfalls observed in this phase include incomplete custom code assessment, underestimating pricing redesign effort, and delaying credit management alignment. Addressing these early reduces downstream rework and testing cycles.
3.2 Phase 2 – Blueprint and Design
This phase defines the future-state SD solution and operating model.
3.2.1 Business Partner Model
The Business Partner model is a fundamental change in S/4HANA. Customer master data is integrated into a unified BP framework with clearly defined roles, credit segments, and sales area assignments.
3.2.2 Pricing Design
Pricing structures must be validated and adjusted to align with the S/4HANA data model. This includes access sequences, routines, tax determination, and integration with Condition Contract Management for accruals.
3.2.3 Advanced ATP (aATP)
In addition, S/4HANA introduces advanced ATP capabilities such as product substitution, backorder processing, supply protection, and confirmation strategies.
3.2.4 FSCM Credit Management
Financial Supply Chain Management becomes mandatory in S/4HANA. It enables real-time credit exposure monitoring, scoring, risk categorization, and automated credit blocking.
3.2.5 Output Management
Output management is redesigned using BRF+ and Adobe Forms. This applies to billing documents, deliveries, and compliance-related outputs.
3.2.6 Billing Design
Billing processes must be reviewed for intercompany billing, debit and credit memos, export billing, and revenue posting logic changes.
3.2.7 Logistics Execution
In addition, logistics execution processes such as delivery processing, route determination, batch management, and third-party logistics integration must be validated, especially when integrated with EWM or TM.
3.2.8 Condition Contract Management
Condition Contract Management replaces legacy rebate agreements. It supports flexible settlement cycles, accurate accruals, and improved audit controls.
Therefore, legacy rebate agreements must be settled and closed before migration, as they cannot be automatically converted. Projects that postpone this activity often face cutover delays and financial reconciliation issues.
3.2.9 Advanced Returns Management
Advanced Returns Management introduces a redesigned returns process covering return requests, inspections, automated refunds, and credit memo proposals.
Existing ECC return processes require redesign and revalidation in S/4HANA.
3.2.10 Advanced Intercompany Processing
S/4HANA enhances intercompany sales and stock transfer order processes with automated billing, unified document flow, real-time valuation, and improved logistics integration.
3.3 Phase 3 – Build and Configure
During SAP SD migration from ECC to S/4HANA, configuration and testing must be aligned closely with redesigned processes. This phase includes configuration and development for:
- SD organizational structures
- Order management and pricing
- Output forms and ATP
- FSCM credit management
- Condition Contract Management
- Advanced Returns Management
- Intercompany processes
End-to-end SD test cycles must be executed, covering order-to-cash, pricing, delivery, billing, and integration scenarios.
3.4 Phase 4 – Test and Validate
Teams must perform comprehensive testing across SD, CCM, ARM, and intercompany processes to validate business scenarios and financial postings.
3.5 Phase 5 – Cutover and Go-Live
Cutover activities include:
- Business Partner migration
- Pricing and open order migration
- FSCM activation
- Output activation
- Closure of ECC rebate agreements
- Activation of ARM and intercompany processes
3.6 Phase 6 – Stabilize and Optimize
Post-go-live stabilization focuses on pricing accuracy, ATP confirmations, output consistency, credit exposure alignment, EDI processing, and settlement tuning. As a result, dedicated hypercare governance during this phase is critical to achieving business confidence and system stability.
4. SD Tools and Utilities
Common tools used during migration include:
- Business Partner conversion tools
- FSCM credit management tools
- Condition Contract Management settlement workbench
- Advanced Returns Management applications
- aATP cockpit
- Migration Cockpit or SAP Data Services
- EDI monitoring tools
- Adobe form design tools
5. SD Migration Timeline
Typical timelines depend on landscape complexity:
- Medium complexity projects: 7 to 10 months
- Large multi-entity rollouts: 12 to 18 months
6. Conclusion
A well-planned SAP SD migration from ECC to S/4HANA enables organizations to stabilize operations and prepare for future innovation. A successful SAP S/4HANA SD migration depends on a strong blueprint, early validation of pricing, credit, ATP, and returns processes, and disciplined testing across all order-to-cash scenarios. Multiple cutover rehearsals and close collaboration between SD, Finance, Logistics, and technical teams are essential to reduce risk.
Organizations that approach SD migration as a structured transformation, rather than a technical upgrade, realize the full value of S/4HANA more effectively. With the right planning, governance, and execution approach, enterprises can achieve a stable, scalable, and future-ready Sales and Distribution landscape.
About the author
Shiva Shankar Gunda is a Jr. Associate ERP at Quadric IT, working on SAP projects with a focus on SAP S/4HANA and Sales and Distribution processes.
LinkedIn
About Quadric IT
Quadric IT supports enterprises across industries in planning and executing SAP S/4HANA transformations, with a strong focus on Sales and Distribution, Finance, and supply chain processes. Our teams bring hands-on delivery experience across complex SD migrations, including pricing redesign, Business Partner conversion, FSCM credit management, Condition Contract Management, Advanced Returns Management, and intercompany scenarios.
This guide reflects practical lessons from real S/4HANA programs and helps organizations reduce risk, improve delivery predictability, and achieve long-term operational stability.
Further Reading
For readers who want to go deeper into event-driven automation and intelligent exception handling in SAP S/4HANA, our SAP experts have authored a comprehensive book titled “Introducing Situation Handling with SAP S/4HANA”. In this book, Raghu Ram Thatavarthy, Kesari Sai Krishna Sabniveesu, and Priyatham Thatavarthy explain how teams can design and implement Situation Handling to proactively detect issues, trigger business actions, and improve operational responsiveness across S/4HANA processes.
This e-book complements SD migration programs by helping teams move beyond system conversion and toward intelligent, event-driven business operations.


